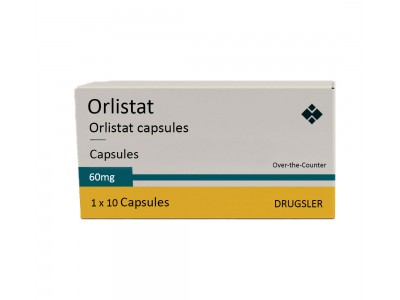
What is Orlistat (Orlistat)?
Orlistat is a medication primarily used to aid in weight loss or to help reduce the risk of regaining weight already lost. It is often prescribed alongside a reduced-calorie diet and exercise program. The drug works by inhibiting the enzyme lipase, which is responsible for breaking down dietary fats in the intestine. By blocking this enzyme, orlistat prevents the absorption of about 30% of the fat consumed in a meal. This undigested fat is then eliminated from the body through bowel movements. The medication is available in both prescription form, typically at a 120 mg dosage under the brand name Xenical, and over-the-counter form at a lower dose of 60 mg, marketed as Alli.
Orlistat is indicated for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, or those with a BMI of 27 or higher who have other risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia. The effectiveness of orlistat can vary, but clinical studies have shown that when combined with a healthy diet and exercise, it can lead to a modest increase in weight loss compared to diet and exercise alone. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues such as oily or fatty stools, frequent bowel movements, and flatulence. These side effects are generally mild and tend to diminish over time as the body adjusts to the medication. However, orlistat can also interfere with the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, so users are often advised to take a multivitamin supplement containing vitamins A, D, E, and K at least two hours before or after taking the medication.
Orlistat is not suitable for everyone, including individuals with chronic malabsorption syndrome or cholestasis, and it should be used with caution in those with a history of kidney stones. It is important for users to follow their healthcare provider’s guidance regarding diet, exercise, and supplementation to maximize the benefits and minimize potential risks associated with the medication.
What is Orlistat (Orlistat) used for?
Orlistat is used primarily to aid in weight loss and to help prevent the regaining of weight that has already been lost. It is commonly prescribed as part of a comprehensive weight management program that includes a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity. By inhibiting the enzyme lipase, orlistat prevents the absorption of about 30% of the fat consumed in a meal, thereby reducing caloric intake and promoting weight loss. This makes it particularly useful for individuals who are obese, with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, or those who are overweight with a BMI of 27 or higher and have additional risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia.
The medication is available both as a prescription drug under the brand name Xenical, which is typically prescribed at a 120 mg dosage, and as an over-the-counter product called Alli, available at a lower 60 mg dosage. Orlistat's ability to block fat absorption not only assists in weight loss but also contributes to improving other health parameters associated with obesity, such as reducing blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol levels.
By incorporating orlistat into a weight management plan, individuals can achieve more significant weight loss compared to diet and exercise alone. However, the drug must be used in conjunction with lifestyle changes to be effective and sustainable. Additionally, due to its mechanism of action, orlistat can cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as oily stools and frequent bowel movements, especially when the diet is high in fat. Users are often advised to take a multivitamin supplement to compensate for the reduced absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K. It is essential for individuals considering orlistat to consult with their healthcare provider to ensure it is an appropriate and safe option for their specific health needs and weight loss goals.
What should you know before taking Orlistat (Orlistat)?
Before taking orlistat, it's important to be aware of several key factors to ensure its safe and effective use. First, orlistat is designed for adults with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher, or those with a BMI of 27 or higher who have additional risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, or dyslipidemia. It is crucial to follow a reduced-calorie, low-fat diet while taking orlistat, as high-fat meals can increase the likelihood of gastrointestinal side effects such as oily stools, flatulence, and frequent bowel movements.
Orlistat works by blocking the absorption of dietary fats, so it also inhibits the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). To mitigate this, users should take a multivitamin supplement at least two hours before or after taking orlistat. It’s also important to evenly distribute daily fat intake across meals to help manage side effects and improve the drug’s efficacy.
Before starting orlistat, inform your healthcare provider of your full medical history, especially any history of chronic malabsorption syndrome, cholestasis, thyroid disorders, or kidney stones, as orlistat may not be suitable for individuals with these conditions. Additionally, if you have diabetes, you should be aware that weight loss can affect your blood sugar levels, so close monitoring and potential adjustment of diabetes medications may be necessary.
Drug interactions are another consideration. Orlistat can interact with certain medications, such as cyclosporine, levothyroxine, and warfarin. Your healthcare provider may need to adjust dosages or monitor you more closely if you are taking these drugs. Finally, orlistat should not be used during pregnancy, as weight loss offers no potential benefit and may harm the unborn baby.
Understanding these factors and following your healthcare provider’s advice can help you use orlistat safely and effectively as part of a comprehensive weight management plan.
How to take Orlistat (Orlistat)?
To take orlistat effectively and safely, follow these guidelines. Orlistat should be taken three times a day with each main meal that contains fat. It is important to take the medication during the meal or up to one hour after eating. If you skip a meal or eat a meal that does not contain fat, you can skip that dose of orlistat. The typical prescription dosage is 120 mg, while the over-the-counter version is usually 60 mg.
Maintain a nutritionally balanced, reduced-calorie diet that contains approximately 30% of calories from fat. This means that if you consume about 2,000 calories per day, no more than 600 of those should come from fat. Distribute your daily intake of fat, carbohydrates, and protein over three main meals. This helps manage potential gastrointestinal side effects and improves the effectiveness of the medication.
Take a multivitamin supplement that contains vitamins A, D, E, and K at least two hours before or after taking orlistat, as the drug can interfere with the absorption of these fat-soluble vitamins. This ensures you get adequate nutrition while using the medication.
If you are also taking medications such as cyclosporine or levothyroxine, take them at least three to four hours before or after orlistat, as it can interfere with their absorption. Your healthcare provider may provide specific instructions based on your individual treatment plan and any other medications you are taking.
Stay hydrated and monitor for side effects, such as changes in bowel habits, which are common when starting orlistat. These side effects often diminish as your body adjusts to the medication. Consult your healthcare provider if you experience persistent or severe side effects.
Follow your healthcare provider’s advice and attend regular check-ups to monitor your progress and adjust your treatment plan as necessary. By adhering to these guidelines, you can maximize the benefits of orlistat while minimizing potential risks and side effects.
Interactions of Orlistat (Orlistat)
Orlistat can interact with several medications, which may affect its efficacy or increase the risk of adverse effects. One of the primary concerns is its interaction with fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). Since orlistat inhibits the absorption of dietary fats, it also reduces the absorption of these essential vitamins. Users are often advised to take a multivitamin supplement at least two hours before or after taking orlistat to ensure adequate nutrition.
Orlistat can also interact with cyclosporine, a medication used to prevent organ transplant rejection. The absorption of cyclosporine can be reduced when taken with orlistat, potentially decreasing its effectiveness. To manage this interaction, cyclosporine should be taken at least three hours before or after orlistat, and blood levels of cyclosporine should be monitored more frequently during concurrent use.
Another important interaction is with levothyroxine, a thyroid hormone replacement therapy. Orlistat can interfere with the absorption of levothyroxine, leading to reduced thyroid hormone levels. Patients taking both medications should take levothyroxine at least four hours before or after orlistat, and thyroid function should be monitored regularly to ensure proper dosing.
Warfarin, an anticoagulant, can also interact with orlistat. Since orlistat affects the absorption of vitamin K, which plays a key role in blood clotting, it can alter the effectiveness of warfarin. Patients on both medications should have their blood clotting parameters (INR) monitored closely to avoid potential bleeding complications or inadequate anticoagulation.
Additionally, orlistat may interact with certain diabetes medications, such as insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents. Weight loss induced by orlistat can affect blood sugar levels, necessitating adjustments in diabetes medication dosages to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
It is essential to inform your healthcare provider about all medications, supplements, and vitamins you are taking before starting orlistat. This allows for appropriate monitoring and dosage adjustments to avoid potential interactions and ensure the safe and effective use of orlistat as part of your weight management plan.
Side effects of Orlistat (Orlistat)
Orlistat, like any medication, can cause side effects, some of which are more common and generally mild, while others may be more severe. The most frequently reported side effects are gastrointestinal in nature due to the medication's mechanism of action, which inhibits fat absorption. These common side effects include oily or fatty stools, increased frequency of bowel movements, an urgent need to have a bowel movement, and flatulence with discharge. These symptoms are typically more pronounced when a high-fat diet is consumed and may lessen as the body adjusts to the medication and dietary fat intake is reduced.
Some users may also experience abdominal pain, bloating, and discomfort, which are usually related to the increased fat content in the digestive system. These gastrointestinal issues are often the most bothersome but are generally manageable with dietary modifications and adherence to a low-fat diet.
In addition to gastrointestinal effects, orlistat can reduce the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). To mitigate this, it is recommended to take a multivitamin supplement at least two hours before or after taking orlistat to ensure adequate nutrition.
Less common but more serious side effects can occur and should be monitored. These include symptoms of liver injury, such as itching, yellowing of the skin or eyes (jaundice), dark urine, loss of appetite, or upper right abdominal pain. If any of these symptoms occur, it is important to seek medical attention immediately.
Other potential side effects include kidney stones, as orlistat can increase levels of oxalate in the urine, which may contribute to stone formation. This is particularly relevant for individuals with a history of kidney stones or other renal issues.
Orlistat can also interfere with the absorption and effectiveness of certain medications, such as cyclosporine, levothyroxine, and warfarin, which can lead to other side effects or complications. It is crucial to inform your healthcare provider about all medications you are taking to manage potential interactions and side effects effectively.
Overall, while orlistat can be an effective aid in weight loss, users should be aware of its side effects and work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor and manage them. This approach ensures the safe and beneficial use of the medication as part of a comprehensive weight management plan.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.

No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.