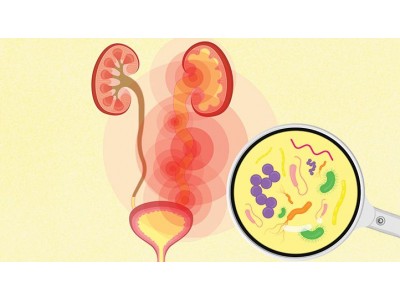
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is typically treated with antibiotics to clear the bacterial infection. Here are the steps typically involved in treating a UTI:
Diagnosis: Your healthcare provider will confirm the diagnosis through a urine test, which checks for the presence of bacteria or white blood cells indicating an infection. Sometimes, a urine culture may be done to identify the specific bacteria causing the infection and determine which antibiotics will be most effective.
Antibiotic Treatment: Based on the urine test results and the severity of your symptoms, your healthcare provider will prescribe an appropriate antibiotic. Commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTIs include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim), nitrofurantoin (Macrobid), fosfomycin (Monurol), and fluoroquinolones (such as ciprofloxacin or levofloxacin), among others. It's important to take the full course of antibiotics as prescribed, usually for 3 to 7 days depending on the antibiotic and the severity of the infection.
Symptom Management: While the antibiotics work to clear the infection, you can manage symptoms such as pain, discomfort, and fever with over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Drinking plenty of water helps to flush out bacteria from the urinary tract.
Follow-Up: It's important to follow up with your healthcare provider as recommended. They may want to repeat a urine test after treatment to ensure the infection has cleared completely, especially if your symptoms were severe or if you are at risk for complications.
Preventive Measures: To reduce the risk of future UTIs, your healthcare provider may recommend strategies such as drinking plenty of fluids, urinating frequently, and practicing good hygiene (including wiping from front to back). For some individuals, particularly those prone to recurrent UTIs, they may prescribe low-dose antibiotics for a longer period or recommend using post-coital antibiotics.
If you experience recurrent UTIs or if symptoms persist despite treatment, further evaluation by a specialist such as a urologist may be necessary to investigate underlying causes and develop a more comprehensive treatment plan.
It's essential to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect a UTI, as untreated infections can lead to more serious complications such as kidney infections. Following your healthcare provider's guidance and completing the prescribed course of antibiotics are key to effectively treating a UTI and preventing recurrence.