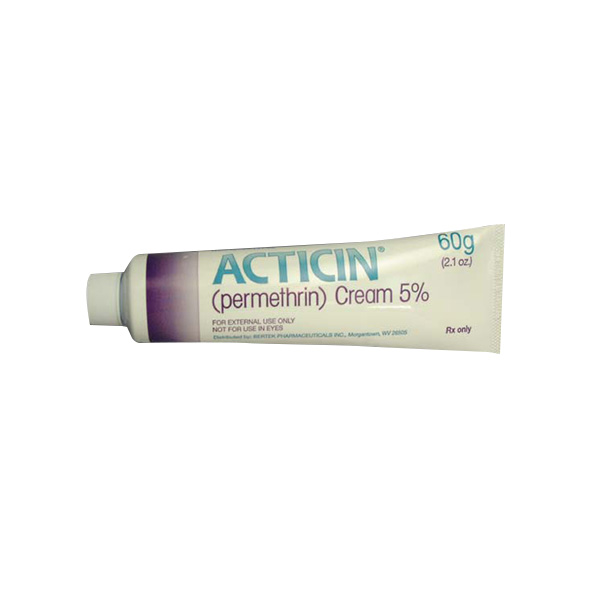
What is Acticin (Permethrin)?
Acticin, whose active ingredient is permethrin, is a topical medication primarily used to treat scabies and lice infestations. Permethrin belongs to a class of drugs known as pyrethrins, which are synthetic chemicals derived from the natural insecticidal properties of chrysanthemum flowers. As a highly effective antiparasitic agent, permethrin works by interfering with the nervous system of scabies mites and lice, leading to paralysis and death of these parasites.
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which burrows into the skin, causing intense itching and rash. Lice are parasitic insects that infest the hair and scalp, leading to itching and irritation. Acticin, when applied to the skin, targets these pests by disrupting their sodium channels, essential for the transmission of nerve signals. This disruption results in the paralysis of the parasites, ultimately leading to their death.
Acticin is available as a cream, usually in a 5% concentration for scabies treatment. The cream is applied in a thin layer over the entire body, from the neck down to the toes, and left on the skin for about 8 to 14 hours before being washed off. For the treatment of lice, permethrin is typically available as a 1% lotion or cream rinse, applied to damp hair and left on for 10 minutes before rinsing out.
The effectiveness of Acticin in treating scabies and lice has made it a widely prescribed treatment. Clinical studies and extensive use in various populations have demonstrated its high efficacy and safety profile. However, while permethrin is generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience mild side effects such as skin irritation, redness, or a burning sensation. These side effects are typically temporary and resolve after discontinuing the treatment.
To enhance the success of the treatment, it is essential to follow specific guidelines. For scabies, all household members and close contacts should be treated simultaneously to prevent re-infestation. Additionally, bedding, clothing, and personal items should be washed in hot water and dried on a high heat setting or sealed in plastic bags for at least 72 hours to kill any remaining mites or eggs. For lice treatment, it is crucial to comb the hair with a fine-toothed comb to remove dead lice and nits after the application of the cream rinse.
While Acticin is highly effective, certain precautions should be observed. It is not recommended for use in individuals who are allergic to permethrin or any of its components. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using Acticin, although studies have not shown significant risks associated with its use during pregnancy. Moreover, permethrin should be used with caution in infants younger than two months.
Despite its effectiveness, there have been reports of resistance to permethrin among lice populations in some regions, potentially reducing its efficacy. In such cases, alternative treatments or combination therapies may be necessary to achieve successful eradication of the infestation. Regular monitoring and consulting with a healthcare provider are essential to ensure the most effective treatment approach.
In conclusion, Acticin (permethrin) is a highly effective and widely used treatment for scabies and lice infestations. Its ability to disrupt the nervous system of parasites, leading to their paralysis and death, makes it a powerful tool in managing these conditions. With proper application and adherence to treatment guidelines, Acticin can significantly alleviate the symptoms and eradicate the infestations, improving the quality of life for affected individuals.
What is Acticin (Permethrin) used for?
Acticin, which contains the active ingredient permethrin, is a topical medication used to treat two primary conditions: scabies and lice infestations. Both conditions involve parasitic organisms that cause significant discomfort and require effective treatment to alleviate symptoms and prevent further spread.
Scabies is a skin infestation caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei mite. These microscopic mites burrow into the upper layer of the skin, leading to severe itching, a rash, and in some cases, secondary bacterial infections from scratching. The infestation is highly contagious and can spread through close personal contact or by sharing contaminated items such as clothing and bedding. Acticin is used to manage scabies by applying the permethrin cream directly to the skin. Permethrin works by disrupting the nervous system of the mites, leading to their paralysis and death. The cream is applied in a thin layer over the entire body, from the neck down to the toes, and left on for about 8 to 14 hours before being washed off. This treatment effectively eliminates the mites and their eggs, providing relief from the intense itching and rash associated with scabies.
Lice infestations, which can occur on the scalp, body, or pubic area, are another common use for Acticin. Head lice, the most prevalent type of lice infestation, cause itching and discomfort due to their bites. These parasites feed on blood and lay their eggs (nits) on the hair shafts, making them challenging to remove. Permethrin, in a lower concentration of 1% as a lotion or cream rinse, is used to treat head lice. The product is applied to the damp hair and left on for 10 minutes before being rinsed out. The permethrin works by disrupting the nerve function of the lice, leading to their death. For body lice and pubic lice, similar principles apply, although treatment may require different formulations or additional measures to ensure complete eradication.
Acticin’s effectiveness in treating these parasitic infestations is well-documented through numerous clinical studies. It is considered a first-line treatment due to its ability to rapidly and effectively eliminate the parasites and their eggs. However, while Acticin is generally safe and well-tolerated, some users may experience mild side effects such as skin irritation, redness, or a burning sensation at the application site. These side effects are usually temporary and resolve once the treatment is discontinued.
To maximize the effectiveness of Acticin, it is crucial to follow treatment guidelines meticulously. For scabies, all close contacts and household members should also be treated simultaneously to prevent re-infestation. Additionally, personal items such as bedding and clothing should be washed in hot water and dried on high heat to kill any mites that might have come into contact with these items. For lice, it is important to use a fine-toothed comb to remove dead lice and nits from the hair after applying the treatment.
While Acticin is highly effective, there are occasional reports of resistance to permethrin among lice populations in certain areas, which can reduce its efficacy. In such cases, alternative treatments or combination therapies may be necessary to achieve successful results. It is also important for pregnant or breastfeeding women to consult with their healthcare provider before using Acticin, although its use has not been associated with significant risks during these periods.
In summary, Acticin (permethrin) is a versatile and effective medication used to treat scabies and lice infestations. By targeting the parasites' nervous systems, it provides relief from symptoms and helps in eradicating these troublesome conditions. Proper use and adherence to treatment guidelines are essential for achieving the best outcomes and ensuring complete resolution of the infestations.
What should you know before taking Acticin (Permethrin)?
Before using Acticin, which contains permethrin, there are several important considerations to keep in mind to ensure its safe and effective use. Acticin is primarily used for treating scabies and lice infestations, and understanding its proper use and potential risks is crucial for successful treatment.
Firstly, it is essential to know that Acticin should be used only as directed by a healthcare provider. For scabies, the permethrin cream is applied to the entire body, from the neck down, and left on for 8 to 14 hours before being washed off. For lice infestations, the permethrin lotion or cream rinse is applied to damp hair and left on for 10 minutes before rinsing. Adhering strictly to these guidelines is vital to ensure the medication's effectiveness and to avoid unnecessary side effects or inadequate treatment.
Before starting treatment, inform your healthcare provider if you have any known allergies, particularly to permethrin or other pyrethrin-based compounds. Allergic reactions, though rare, can occur and may manifest as severe itching, rash, or swelling. If you experience any of these symptoms after applying the medication, discontinue use and seek medical advice immediately.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should consult their healthcare provider before using Acticin. While permethrin is generally considered safe for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it's crucial to discuss potential risks and benefits with a healthcare professional. They can provide guidance based on individual health circumstances and the latest medical research.
Acticin should not be used on open wounds, irritated, or inflamed skin. Applying the medication to such areas can increase the risk of systemic absorption and potential side effects. It is also important to avoid applying the cream or lotion to the eyes, mouth, or other mucous membranes. If contact with these areas occurs, rinse thoroughly with water and seek medical advice if irritation persists.
For individuals with a history of skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis, using Acticin may require special consideration. These conditions can potentially alter the skin's absorption of the medication and may lead to increased side effects or reduced efficacy. Your healthcare provider can offer personalized advice on managing these conditions while using Acticin.
When treating scabies, it is crucial to treat all close contacts and household members simultaneously to prevent re-infestation. Scabies is highly contagious, and even after successful treatment, reinfection can occur if others in the household or close contacts are not treated. Additionally, wash all bedding, clothing, and personal items in hot water and dry them on a high heat setting to eliminate any mites that may be present.
For lice infestations, it is important to use a fine-toothed comb to remove dead lice and nits from the hair after treatment. This step helps ensure that all lice and eggs are removed, reducing the risk of reinfestation. If lice are present in other areas, such as the body or pubic region, additional treatment or different formulations may be needed.
Acticin is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience mild side effects such as itching, redness, or a burning sensation at the application site. These effects are typically temporary and resolve after discontinuation of the medication. However, if severe or persistent side effects occur, seek medical attention promptly.
Lastly, be aware that resistance to permethrin has been reported in some lice populations. If the initial treatment is not effective, consult with your healthcare provider for alternative treatment options.
In summary, before using Acticin, it is important to understand the correct usage, potential side effects, and precautions to take. Consulting with a healthcare provider and following treatment guidelines can help ensure the safe and effective management of scabies and lice infestations.
How to take Acticin (Permethrin)?
Using Acticin, which contains permethrin, involves following specific instructions to ensure effective treatment for scabies and lice infestations. Proper application and adherence to guidelines are crucial for the medication's success in eradicating these parasitic conditions.
For the treatment of scabies, Acticin is available as a 5% permethrin cream. The application process begins with ensuring that the skin is clean and dry. Before applying the cream, it is important to wash and dry your body thoroughly. Acticin should be applied to the entire body from the neck down, including the soles of the feet, in a thin, even layer. It is essential to cover all areas, including skin folds and under the nails, where mites may be present. Avoid applying the cream to the face, mouth, or genital areas unless directed by your healthcare provider.
After applying the cream, it should remain on the skin for about 8 to 14 hours. This time frame allows the permethrin to effectively kill the scabies mites and their eggs. It is often recommended to apply the cream before bedtime and then wash it off in the morning. During this time, it is important to avoid bathing, showering, or sweating excessively, as this could potentially reduce the effectiveness of the treatment. Once the designated time has elapsed, thoroughly wash off the cream with water and soap. Make sure to remove all traces of the medication from your skin.
For treating lice infestations, Acticin is available as a 1% permethrin lotion or cream rinse. The application process begins with dampening the hair. Apply the permethrin product evenly to the damp hair and scalp, making sure to cover all areas, including behind the ears and at the nape of the neck. Use enough product to saturate the hair and scalp thoroughly. Leave the product on the hair for about 10 minutes, as this allows sufficient time for the permethrin to act on the lice. After the recommended time has passed, rinse the hair thoroughly with warm water.
It is important to follow up with a fine-toothed comb to remove dead lice and nits (eggs) from the hair after rinsing out the treatment. This step is crucial for ensuring that all lice and eggs are removed, as leftover nits can potentially lead to re-infestation. For body and pubic lice, similar principles apply, but ensure to use appropriate formulations and follow any additional instructions provided by your healthcare provider.
For both scabies and lice treatments, it is essential to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen and avoid using more of the medication than recommended. Overuse can lead to increased risk of side effects or resistance. Additionally, all close contacts and household members should be treated simultaneously to prevent re-infestation of scabies. For lice, it is also important to wash all clothing, bedding, and personal items in hot water and dry them on a high heat setting to kill any lice or eggs that may have come into contact with these items.
If the infestation persists or if you have any concerns about the treatment, consult with your healthcare provider for further evaluation and potential alternative treatments. While Acticin is highly effective, resistance to permethrin has been reported in some lice populations, which may require different therapeutic approaches.
In summary, proper use of Acticin involves applying the cream or lotion as directed, allowing it to remain on the skin or hair for the prescribed time, and following up with additional measures to ensure complete eradication of scabies or lice. Adhering to these guidelines will help maximize the effectiveness of the treatment and ensure a successful outcome.
Interactions of Acticin (Permethrin)
Acticin, which contains the active ingredient permethrin, is a topical medication used primarily for treating scabies and lice infestations. While permethrin is generally well-tolerated and effective, it is important to be aware of potential interactions and considerations to ensure safe and effective use.
Permethrin is a synthetic pyrethroid that works by disrupting the nervous system of parasites, leading to their paralysis and death. As a topical agent, its systemic absorption is minimal when applied according to directions, which generally reduces the likelihood of interactions with other medications. However, there are still some factors to consider.
Firstly, it is crucial to avoid using permethrin in conjunction with other topical treatments that could irritate the skin. For instance, applying other topical medications, such as corticosteroids or other antiparasitic agents, in the same area as Acticin could increase the risk of skin irritation or adverse reactions. It is advisable to allow a period of time between the application of different topical treatments and to consult a healthcare provider if multiple treatments are necessary.
Permethrin should not be used simultaneously with or immediately after applying products that contain alcohol, strong astringents, or other drying agents. These substances can enhance the potential for skin irritation and reduce the effectiveness of the treatment. To avoid such issues, it is recommended to use Acticin as directed and to wait until any other topical products have been fully absorbed or removed before applying permethrin.
For individuals with pre-existing skin conditions such as eczema or psoriasis, there is a potential for increased skin sensitivity when using permethrin. These conditions can alter the skin barrier, potentially leading to more significant absorption of the medication and a higher risk of local irritation or systemic effects. In such cases, it is essential to follow the treatment guidelines carefully and consult a healthcare provider for advice on managing these conditions while using Acticin.
There are no well-documented systemic drug interactions with permethrin due to its limited absorption into the bloodstream. However, if other medications are being used concurrently, particularly those that affect the skin or have known interactions with topical treatments, it is prudent to discuss these with a healthcare provider. This is especially important for individuals undergoing treatment with other prescription or over-the-counter medications.
For pregnant or breastfeeding women, it is generally considered safe to use Acticin, but it is still important to consult a healthcare provider before starting treatment. While there is no substantial evidence indicating adverse effects during pregnancy or lactation, a healthcare provider can offer personalized guidance based on individual health circumstances and ensure that the benefits of using the medication outweigh any potential risks.
In cases where Acticin is used improperly, such as applying excessive amounts of the cream or lotion, there could be an increased risk of skin irritation or systemic absorption. It is important to use the medication exactly as prescribed, avoiding overuse, and to follow all instructions for application and duration of treatment.
In summary, while Acticin (permethrin) generally has minimal systemic interactions due to its topical application, it is important to consider potential local interactions and follow proper usage guidelines. Avoiding concurrent use of other topical treatments that may irritate the skin, consulting with a healthcare provider if there are existing skin conditions, and adhering to prescribed application instructions can help ensure the safe and effective use of Acticin. Always consult with a healthcare provider if there are any concerns or questions about drug interactions or the overall treatment plan.
Side effects of Acticin (Permethrin)
Acticin, which contains permethrin, is a topical medication used primarily for treating scabies and lice infestations. While generally effective and well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some individuals. Understanding these potential side effects can help users manage and address them appropriately.
Common side effects of Acticin include mild to moderate skin reactions. Users might experience itching, redness, or a burning sensation at the application site. These symptoms are usually temporary and result from the skin's response to the medication. The irritation is typically localized and resolves once the treatment is discontinued and the affected area is washed.
In some cases, individuals might experience more significant skin reactions, such as severe itching, rash, or swelling. These symptoms can indicate an allergic reaction or hypersensitivity to permethrin. While such reactions are rare, they require prompt medical attention. If severe redness, hives, or swelling occurs, especially if it involves areas beyond the application site or is accompanied by difficulty breathing, immediate medical consultation is necessary.
Another potential side effect is dryness or peeling of the skin at the treatment site. This can occur due to the medication's effects on the skin and is usually temporary. Applying a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer after treatment can help alleviate dryness and discomfort.
For those using Acticin to treat lice infestations, the medication is applied to the scalp and hair. Although less common, users might experience scalp irritation, such as itching or redness. Similar to other side effects, these symptoms are generally mild and resolve with the completion of the treatment. If the irritation is persistent or severe, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider.
Systemic side effects are rare with Acticin due to its minimal absorption into the bloodstream. However, if the medication is used excessively or applied to broken skin, the risk of systemic absorption and potential side effects increases. Systemic reactions could include dizziness, headache, or gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, though these are uncommon.
In very rare instances, individuals might experience more severe adverse effects. If symptoms such as severe headache, tremors, or convulsions occur, it could suggest an unusual reaction to the medication. In such cases, discontinuing use and seeking immediate medical attention is essential.
It is also important to monitor for signs of secondary infections. If intense scratching or irritation leads to breaks in the skin, there is a risk of bacterial infection. Signs of infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, or discharge from the affected area. Should these symptoms arise, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate management, which may include antibiotic treatment.
For pregnant or breastfeeding women, although Acticin is generally considered safe, any medication use should be discussed with a healthcare provider. This ensures that the potential benefits of using the medication outweigh any possible risks to the mother or infant.
In summary, while Acticin (permethrin) is an effective treatment for scabies and lice, it can cause side effects ranging from mild skin irritation to more severe reactions in rare cases. Most side effects are localized and resolve with proper use and discontinuation of the medication. Monitoring for unusual or severe symptoms and consulting a healthcare provider as needed can help manage side effects effectively and ensure a successful treatment outcome.
There are no reviews for this product, be the first to leave your review.

No questions about this product, be the first and ask your question.